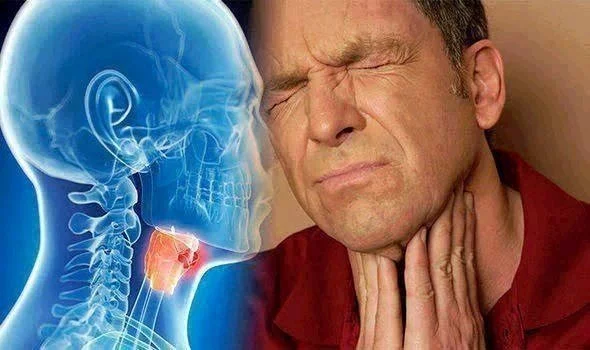
Throat cancer is one of the most aggressive and often overlooked cancers, affecting the throat, voice box, and tonsils. Its silent onset and rapid progression make early detection challenging, with symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, persistent hoarseness, throat pain, or breathing issues often appearing only in advanced stages.
Primary Risk Factors: Smoking and Alcohol.
Medical research consistently points to tobacco use as the leading cause of throat cancer. Whether through cigarettes, cigars, or smokeless tobacco, harmful chemicals damage throat cells, leading to mutations that can trigger cancer.
Heavy alcohol consumption exacerbates the risk by irritating the delicate lining of the throat. Together, smoking and drinking create a dangerous synergy, dramatically increasing the likelihood of developing the disease. Reducing alcohol intake—or avoiding it entirely—can significantly lower your risk.
Other Contributing Factors
• Chewing Tobacco and Other Substances: Chewing tobacco, khat (miraa), and similar substances expose the oral cavity to carcinogens directly, sharply raising the risk of throat and oral cancers.
• Dietary Habits: A diet lacking fresh fruits and vegetables diminishes the body’s ability to defend against cellular damage. Nutrients like vitamins A, C, and E help protect throat tissue and reduce cancer risk.
• HPV Infection: Human Papillomavirus (HPV), transmitted through unprotected oral sex, has been identified as a major cause of certain types of throat cancer, emphasizing the importance of safe sexual practices.
• Poor Oral Hygiene: Chronic irritation from untreated dental issues or infections can contribute to the development of malignant cells in the throat and oral cavity.
Prevention: The Most Effective Defense
Prevention remains the most reliable strategy against throat cancer. Key steps include:
1. Quit or Avoid Tobacco: Eliminating smoking and chewing tobacco dramatically reduces cancer risk.
2. Moderate Alcohol Consumption: Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining entirely lowers irritation and cellular damage.
3. Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet: Incorporate fresh fruits, vegetables, and foods high in vitamins A, C, and E to bolster natural defenses.
4. Practice Safe Sex: HPV vaccination and safe oral sexual practices help prevent virus-related throat cancers.
5. Maintain Oral Health: Regular dental check-ups and proper hygiene reduce chronic irritation and potential risk factors.
6. Stay Hydrated and Healthy: Adequate hydration and a balanced lifestyle strengthen overall immunity and resilience.
By adopting these proactive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing throat cancer and safeguard their long-term health. Early awareness, lifestyle adjustments, and routine medical check-ups remain critical in fighting this potentially life-threatening disease.