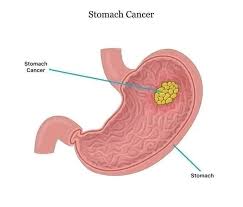
Stomach cancer remains one of the deadliest forms of cancer, largely because it often develops silently and is diagnosed only at an advanced stage. Early symptoms such as persistent indigestion, bloating, abdominal discomfort, or nausea are frequently mistaken for minor digestive problems, delaying medical attention.
Medical research shows that daily lifestyle and dietary habits play a significant role in either increasing or reducing the risk of stomach cancer. Among the most notable risk factors are the following:
1. Frequent Consumption of Processed and Smoked Foods
Processed and smoked foods such as sausages, bacon, hot dogs, and smoked fish contain nitrates and nitrites, chemicals used to preserve food. Inside the stomach, these substances can form harmful compounds that damage stomach cells and irritate the stomach lining over time.
While occasional consumption may pose minimal risk, diets that rely heavily on processed meats have been associated with a higher likelihood of stomach-related diseases. Health experts recommend prioritising fresh, minimally processed foods whenever possible.
2. Excessive Salt Intake
High salt consumption can weaken the stomach’s natural protective barrier, making it more vulnerable to damage and infection. Excess salt also promotes the growth of Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium strongly linked to stomach cancer.
Salty snacks, pickled foods, preserved meals, and heavily seasoned dishes should be eaten in moderation to protect long-term stomach health.
3. Regular or Heavy Alcohol Use
Alcohol irritates the stomach lining and reduces its ability to repair itself. Frequent or excessive alcohol consumption increases inflammation and makes the stomach more susceptible to harmful substances, raising the risk of cancer and other digestive disorders over time.
Protecting Stomach Health
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, staying well hydrated, and limiting alcohol and salt intake can significantly reduce the risk of stomach-related illnesses. Regular medical checkups and early evaluation of persistent digestive symptoms are also critical for early detection and prevention.
Adopting healthier eating habits not only lowers cancer risk but also promotes overall digestive and long-term wellbeing.