Diseases affect our bodies and how they work. While medicine has made great progress in curing many illnesses, some diseases remain incurable. Although treatments can help manage symptoms or slow disease progress, these six illnesses have no permanent cure.
Here is what you should know about these serious diseases and what causes them.
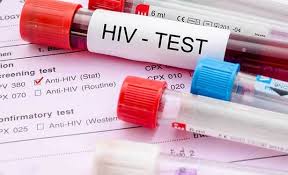
HIV/AIDS
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) attacks the immune system, weakening the body’s defense against infections. If untreated, it develops into AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), where the immune system is very weak.
Causes: HIV spreads mainly through bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, anal mucus, and breast milk. Common ways of infection include unprotected sex, sharing needles, and mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Treatment: Antiretroviral therapy (ART) helps people live longer, healthier lives but does not cure HIV.
Cancer
Cancer happens when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the body, affecting organs like lungs, breasts, or prostate.
Causes: Cancer is caused by genetic mutations, which can be inherited, or triggered by factors such as radiation and chemicals. It is not contagious.
Treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation can manage cancer. A cure means all cancer is gone forever, but remission means the cancer is under control or hidden and might return.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot properly control blood sugar levels.
Types: Type 1 (body produces little or no insulin) and Type 2 (body cannot use insulin well).
Causes: Type 1 is often genetic and autoimmune, while Type 2 is linked to genetics, lifestyle, and insulin resistance.
Treatment: Insulin injections and lifestyle changes help manage diabetes, but there is no cure.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease causes memory loss and thinking difficulties, worsening over time and leading to dementia.
Causes: It happens due to buildup of abnormal proteins in the brain, damaging nerve cells. Age, genetics, family history, and poor heart health increase risk.
Treatment: Current treatments can slow symptoms but cannot stop or reverse the disease.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Also called Lou Gehrig’s disease, ALS affects nerve cells controlling muscles, causing loss of movement, speech, and eventually breathing.
Causes: The exact cause is unknown but may be a mix of genetics and environment. It does not spread between people.
Treatment: There is no cure, and the disease steadily worsens.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s affects movement with symptoms like tremors, stiffness, and balance problems.
Causes: Damage or death of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. Genetics and environmental toxins may play a role.
Treatment: Medicines and therapies help control symptoms, but there is no cure.
While these diseases cannot be cured yet, early detection, proper treatment, and healthy lifestyle choices can improve quality of life and slow disease progression. Awareness of their causes helps with prevention and better care.
If you want to stay updated on health news and advice, follow Tribune Online for more information.